BAD ASS BCAA 8:1:1 400g
BAD ASS® BCAA 8:1:1
Contains sweeteners and a branched-chain amino acid complex with a quantitative ratio of 8:1:1. It is designed for physically active people. It provides three key amino acids essential for building musculature. To ensure fast recovery andmuscle growth, it is essential to provide the body with an adequate dose of branched-chain amino acids.
BAD ASS BCAA 8:1:1
Supplement containing branched-chain amino acids in a ratio of 8:1:1, with leucine having a predominantly anabolic effect. This formula features a significantly higher amount of leucine, making it exhibit pronounced anabolic properties. Leucine has a direct effect on muscle protein synthesis and is crucial for those seeking to increase muscle mass.
The product offers :
- Eight times more leucine
- Strong anabolic effect
- Supporting the growth of muscle mass
- Rapid post-exercise recovery
- Definitely more effective than standard BCAAs
Product composition 8:1:1 :
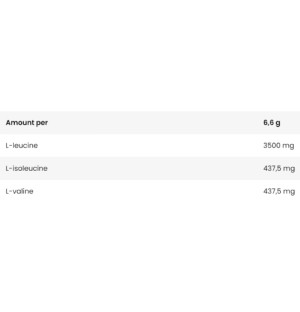
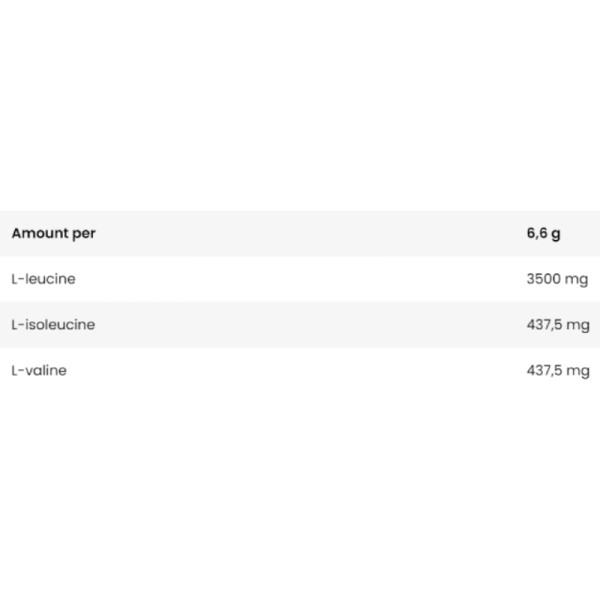
L-leucine - 3500 mg - Leucine, together with isoleucine and valine, forms an important part of the branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) group. It is a key amino acid responsible for anabolic processes in the body. Leucine acts as 'fuel' for muscles during physical activity and supports the synthesis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy source in muscle cells.
L-valine - 437.5 mg - during prolonged exercise, blood glucose levels are reduced and glycogen stores are depleted. The body draws valine, leucine and isoleucine from the muscles to replenish energy stores and keep the muscles working. The process of gluconeogenesis involves the conversion of valine to glucose in the liver. By supplying valine to the muscles, the loss of branched-chain amino acids from the muscles is reduced. Valine reaches the muscle tissues, which helps to reduce catabolism. This is because our muscles will first use the BCAAs consumed as a dietary supplement.
L-isoleucine - 437.5 mg - isoleucine is an organic chemical molecule that is an isomer of leucine. It is an aliphatic amino acid present in virtually all proteins of the body. The highest concentrations of isoleucine are found in blood plasma proteins and human haemoglobin. Isoleucine is one of the essential amino acids required for the production of proteins such as haemoglobin, which is responsible for transporting oxygen to all cells in the body. In strength-training individuals, the proper development of muscle tissue is partly dependent on the availability of isoleucine.
Recommended dosage :
One 6.6 g serving after training.
Calculator for measuring research doses
Tip: 1 MG = 1000 MCG